Turmeric, a golden plant for our health Turmeric is an orange root that has been used in curries and as a medicinal plant in India for thousands of years. Its components with active properties are mainly curcuminoids, of which curcumin is one. According to several studies, turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties,1,2 which can make […]

Osteoporosis
What is osteoporosis? Osteoporosis is a widespread skeletal disease (1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men over the age of 50): the bone becomes demineralized because calcium and phosphorus can no longer bind. Bone resorption becomes faster than its renewal, which weakens the bone, predisposes to fractures and reduces quality of life. What […]

Building blocks for cartilage, tendons, ligaments & skin
The tissues of cartilage, tendons and ligaments have strong common features. In scientific language they are part of the “extra cellular matrix” and in everyday life they are known as “connective tissue”. The building blocks of connective tissue are the same for cartilage, tendons, ligaments and skin (especially in the subcutaneous layers, the hypodermis): collagen […]
Read More… from Building blocks for cartilage, tendons, ligaments & skin

Sports injuries, how to recover well?
Tendinitis, sprains, fractures, dislocations but also muscle tears are common, in athletes as well as in amateur sportsmen and women. After a sports injury, there are many points to consider in order to recover as well as possible. The affected area must regain its functions (range of motion, strength, control) without pain or inflammation. Muscles […]
What is oxidative stress?
Oxidation, how does it work? Oxidation is a chemical reaction that takes place in the presence of oxygen. You can see it when you cut an apple: once cut, the apple tends to turn brown because one of its enzymes reacts with oxygen and transforms a molecule (called phenol) into another molecule (called quinone) which […]
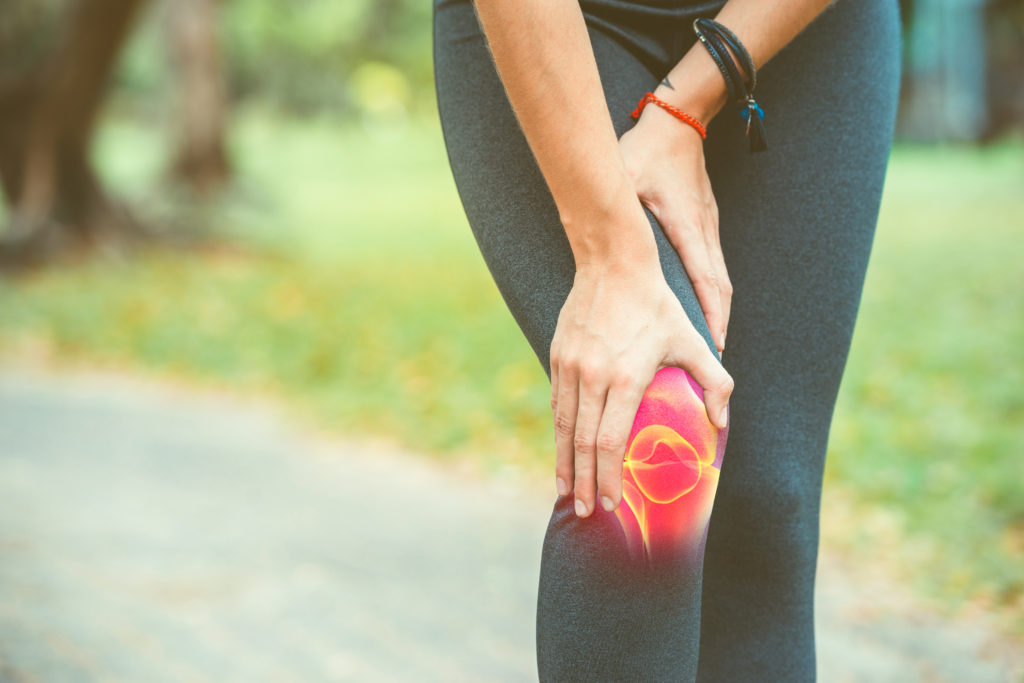

Nutrients for the joints: cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bones
Collagen I, II, III Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and in mammals. It forms fibres in the extracellular matrix, giving shape and mechanical properties to tissues. There are 28 types of collagen in our body, of which the first 3 are the most abundant. Type I collagen is mainly present […]
Read More… from Nutrients for the joints: cartilage, tendons, ligaments, bones
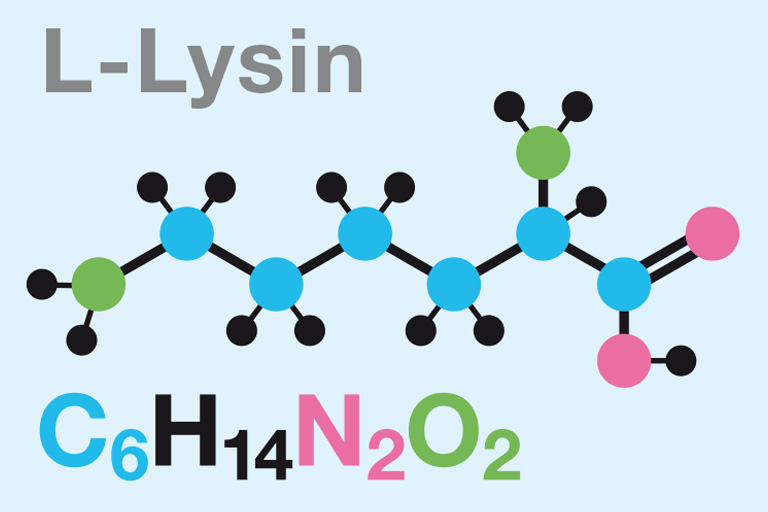
Lysine and threonine: essential amino acids important for the connective tissue
Lysine Lysine is an essential amino acid, which means that our body cannot make it and therefore we must obtain it through our nutrition. Lysine increases the absorption of calcium in the intestines and limits its evacuation through the urine, which helps maintain healthy bones. Lysine also promotes healthy blood vessels and smooth muscles and […]
Read More… from Lysine and threonine: essential amino acids important for the connective tissue

What is MSM ?
MSM (methylsulfonylmethane) is a natural organo-sulphur compound found in certain fruits, vegetables and grains. Nutrients close to MSM can be converted to MSM by intestinal bacteria, but not everyone has these bacteria.1 Taking a dietary supplement containing MSM directly may therefore be the best, safe and well-tolerated option. What are the properties of MSM? Due […]
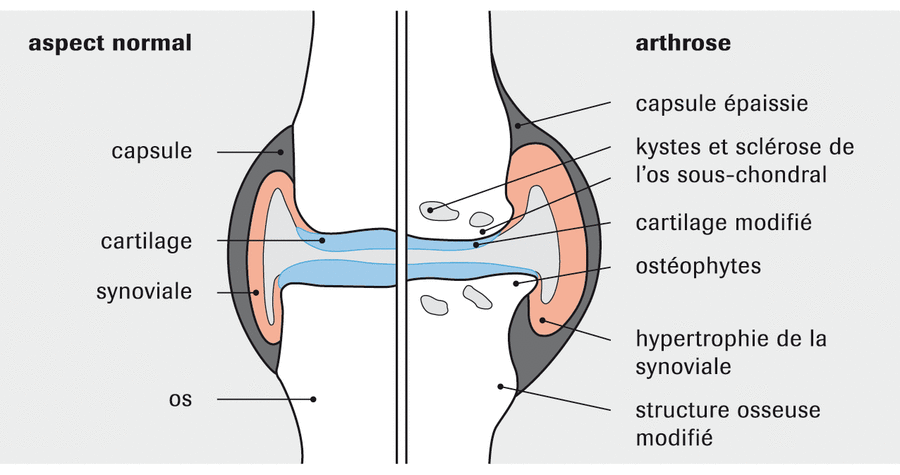
Osteoarthritis: causes and effects
What is osteoarthritis? A joint is made up of two (or more) bones, the ends of which are called subchondral bones. The end of each bone is covered in cartilage, which absorbs mechanical shock and is composed of extracellular matrix (type II collagen and aggrecans: hyaluronic acid + chondroitin). The area where the two bones are closest together is […]

The benefits of taking oral hyaluronic acid
What is hyaluronic acid? Hyaluronic acid is one of the main components of the extracellular matrix. It binds with chondroitin and keratan sulphate, and forms crosslinks with collagen fibres. It is a glycosaminoglycan made in the synoviocytes, fibroblasts and chondrocytes, and plays an important role in the biomechanical properties of connective tissue. It has excellent […]
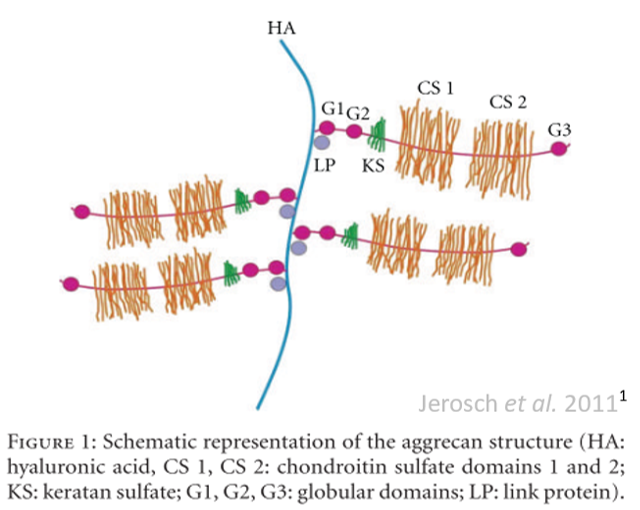
Glucosamine and chondroitin: partners of the extracellular matrix
What are glucosamine and chondroitin? Glucosamine is a monosaccharide that occurs naturally in our bodies. It is the precursor to a number of glycosaminoglycans such as hyaluronic acid, chondroitin and keratan sulphate, which in turn make up some important components of the extracellular matrix called aggrecans. Glucosamine can be found in certain foods, but we […]
Read More… from Glucosamine and chondroitin: partners of the extracellular matrix
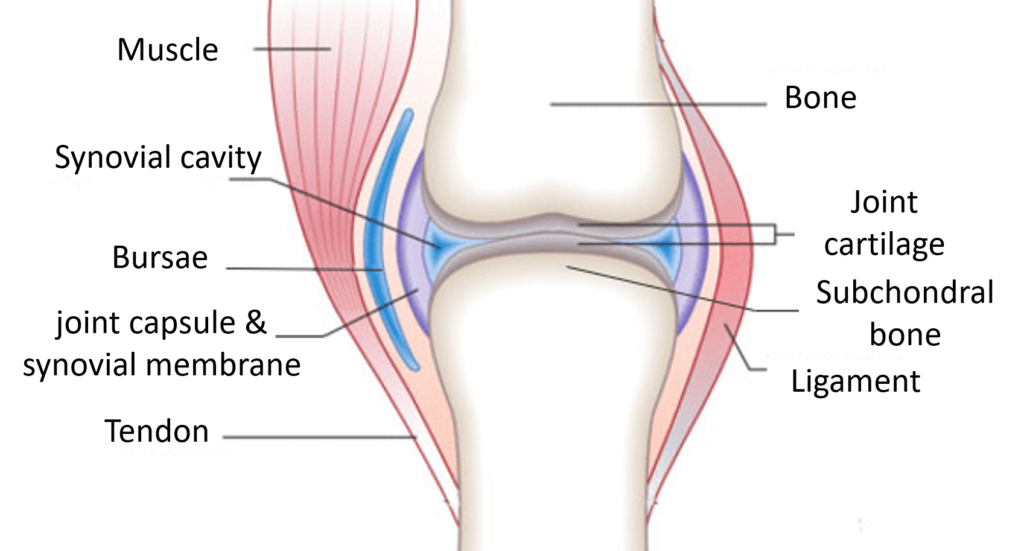
Joint pain
What is a joint? A joint is the point of connection between two (or more) bones. There are different types of joints, which have varying degrees of mobility. The knee, shoulder, hip and fingers are very movable joints, while the vertebrae are less movable, and the joints of the skull are immovable. The tolerated movements […]
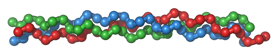
Collagen is essential … but why?
What is collagen? Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and plays a structural role. It is mainly found in connective tissues (skin, bone, cartilage, muscles, vessel walls …). There are 28 types of collagen in our body. All are composed of 3 α chains that form a helix, but each type […]
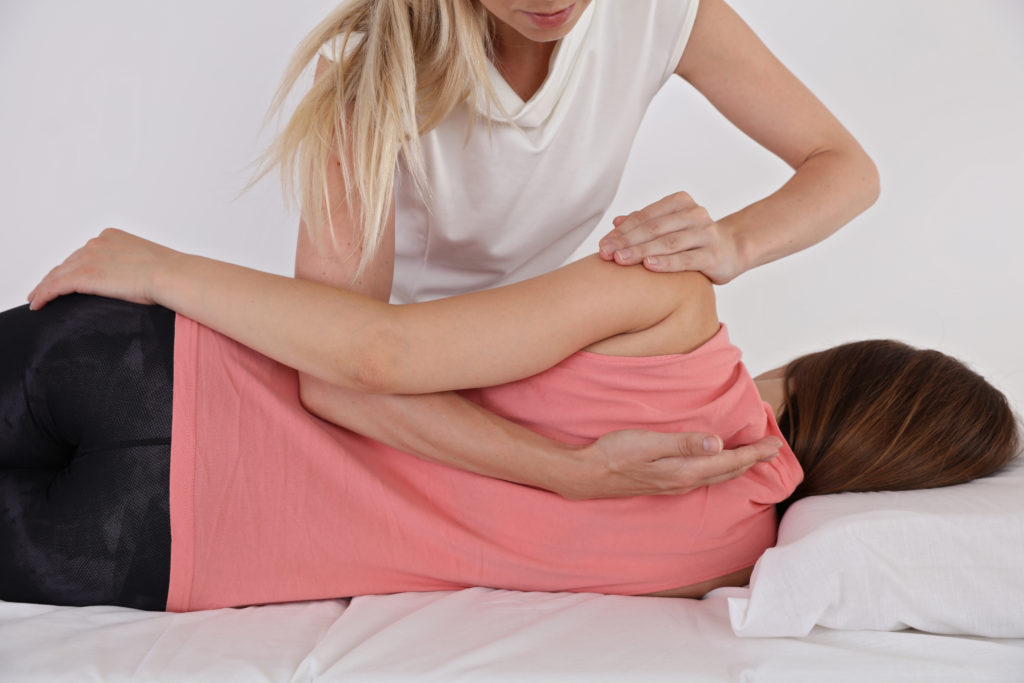

Manual therapies for back pain
On November 28th and 29th, Swiss Alp Health took part in the Swiss Congress of Manual Medicine SAMM (Schweizerische Ärztegesellschaft für Manuelle Medizin) in Interlaken, as manual therapies and certain dietary supplements work in tandem for the maintenance of mobility. Manipulations in manual therapy According to Dr. Med. Melchior Huggler, a specialist in physical medicine […]
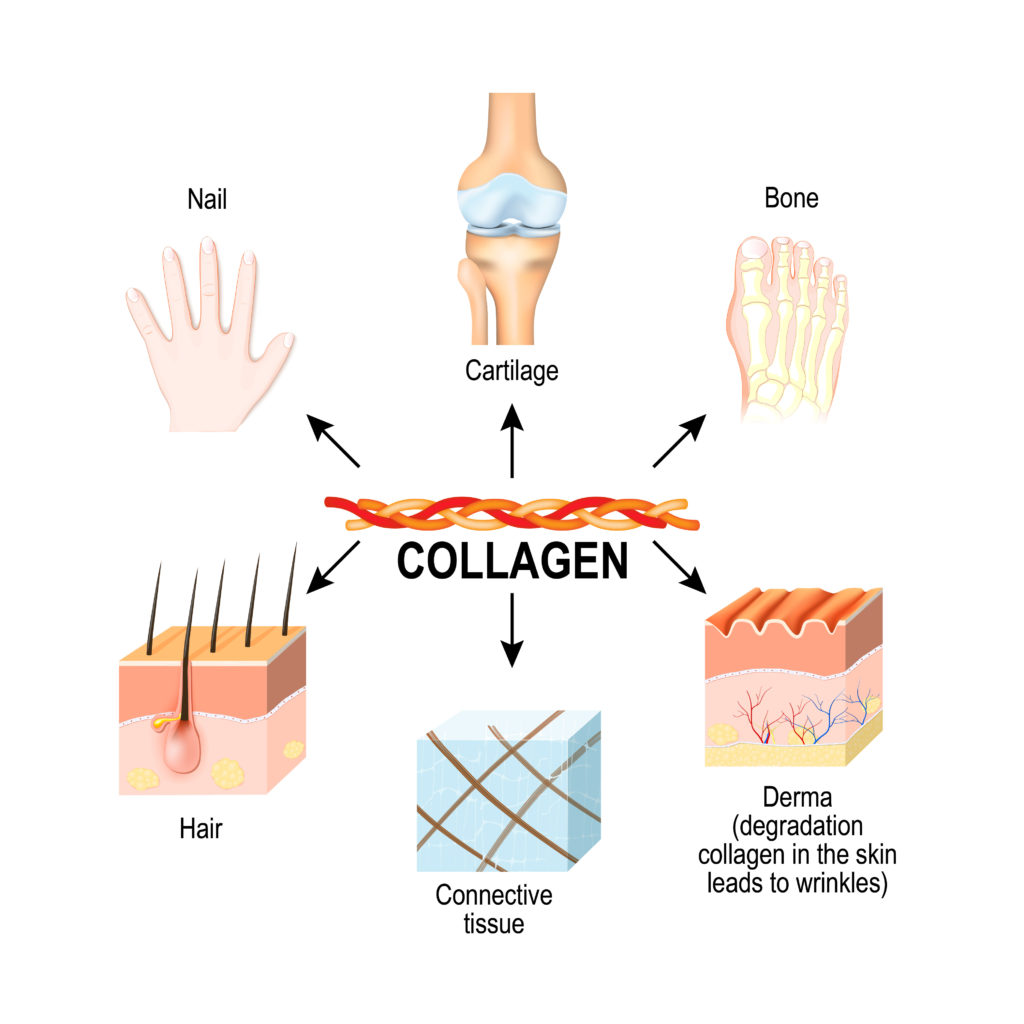
9 health benefits of collagen
Whether it is to support joints or the skin, oral intake of collagen peptides is good for the body. You, too, can benefit from the numerous properties of collagen ! What are the different types of collagen? Collagen is the most dominant protein in the human body and in mammals. It forms fibers in the […]



